Editor's Choice
Improvement in Dissolution of Bosentan Monohydrate by Solid Dispersions Using Spray Drying Technique
Pankaj V. Dangre, Vikesh B. Sormare, Mangesh D. GodboleApril 28, 2017
Other Post
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Stability Indicating Method for the Determination of Bromazepam Via its Copper (II) Chelates
April 28, 2017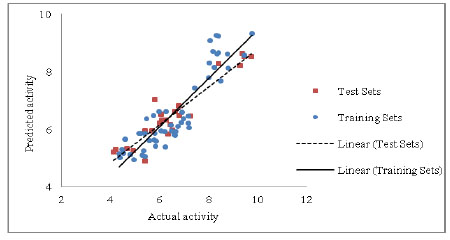
Development and Validation of a Robust QSAR Model For Piperazine and Keto Piperazine Derivatives as Renin Inhibitors
March 31, 2016
Optimization of Bifonazole-Loaded Nisomal Formulation Using Plackett-Burman Design and 23 Factorial Design
May 06, 2016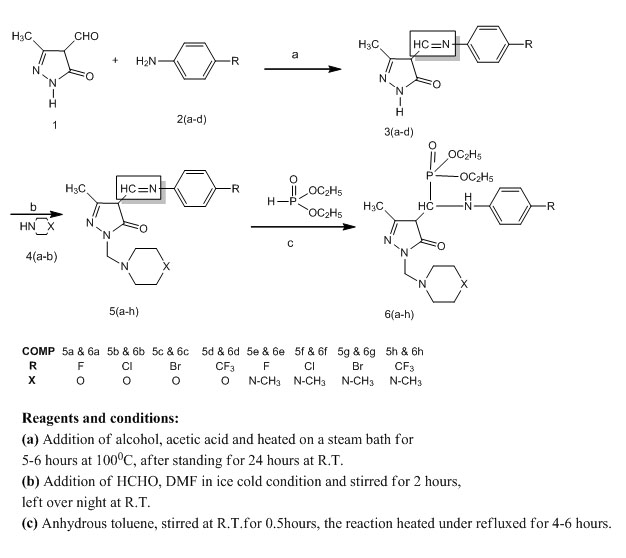
Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Novel Mannich Bases Containing Pyrazole-5-One Phosphonates
May 18, 2016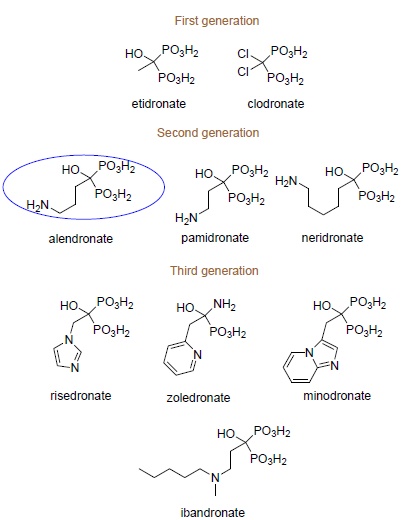
Physiologic Activity of Bisphosphonates – Recent Advances
May 30, 2016
Structural Features of Quercetin Derivatives by Using Pharmaco-phore Modeling Approach
June 06, 2016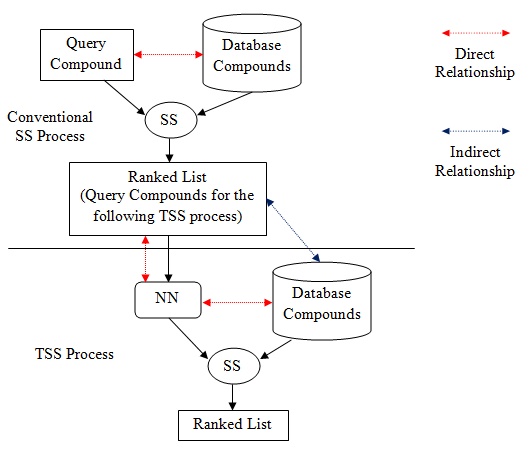
The Effect of Adding Indirect Relationship to Turbo Similarity Searching
June 15, 2016
Microwave Assisted Facile Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 2-Indolyl -1, 5-Benzothiazepines
June 22, 2016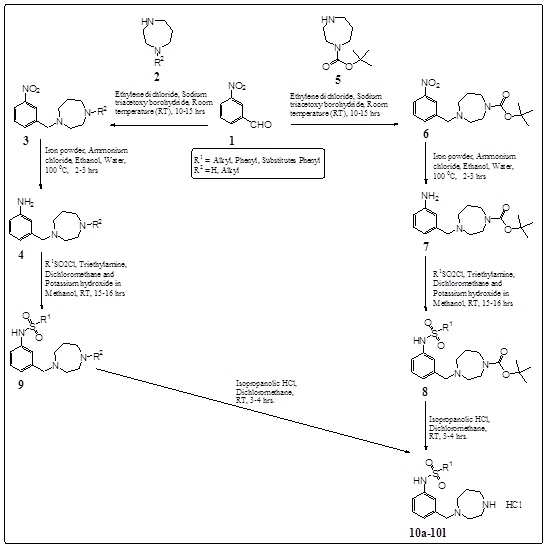
Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Substituted 3-(1, 4-Diazepanyl)-Methyl-Phenyl-Sulphonamides as Potent 5-HT6 Antagonists in Cognitive Disorders
June 30, 2016
Hydroxyl Ethyl Cellulose HHX and Polymethyl Methacrylate Based Site Specific Floating Delivery of Prochlorperazine Maleate
July 28, 2016
Structural Insights into the Molecular Design of HER2 Inhibitors
July 29, 2016
Most Accessed Articles
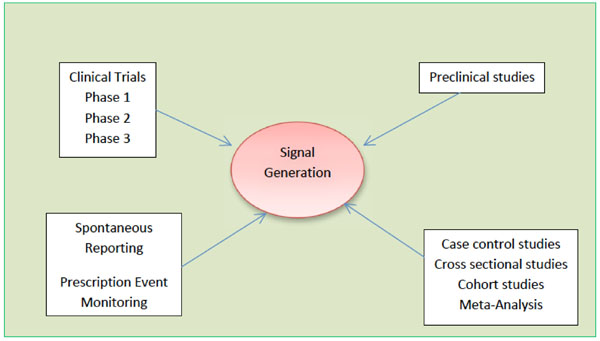
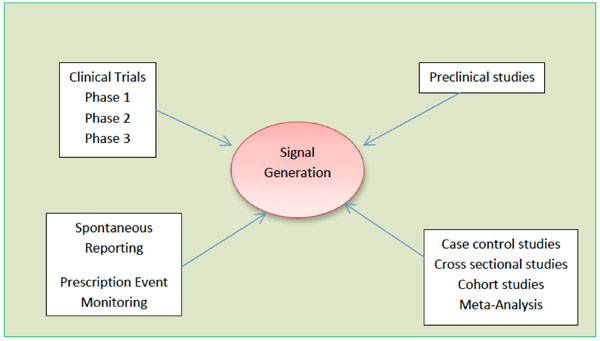
Signal Detection and their Assessment in Pharmacovigilance
Anoop Kumar, Henna Khan
December 17, 2015
Physiologic Activity of Bisphosphonates – Recent Advances
Ewa Chmielewska, Paweł Kafarski
May 30, 2016
Computational Studies on Imidazo[1,2-a] Pyridine-3-Carboxamide Analogues as Antimycobacterial Agents: Common Pharmacophore Generation, Atom-based 3D-QSAR, Molecular dynamics Simulation, QikProp, Molecular Docking and Prime MMGBSA Approaches
Suraj N. Mali, Hemchandra K. Chaudhari
September 28, 2018
Development and Validation of a Robust QSAR Model For Piperazine and Keto Piperazine Derivatives as Renin Inhibitors
Jimish R. Patel, Laxman M. Prajapati
March 31, 2016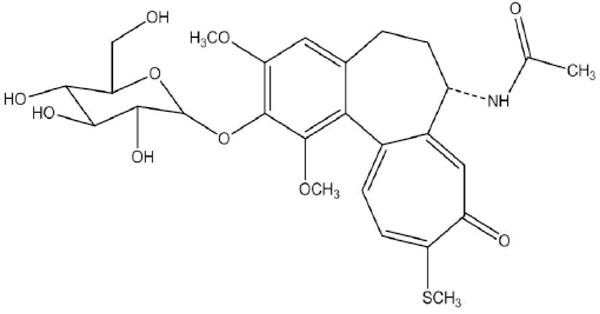
Analytical Methods for Determination of Muscle Relax-ant Thiocolchicoside in Pharmaceutical Preparations- A Review
J.K. Rajput, P.H. Patil, S. J. Surana, A. A. Shirkhedkar
December 8, 2015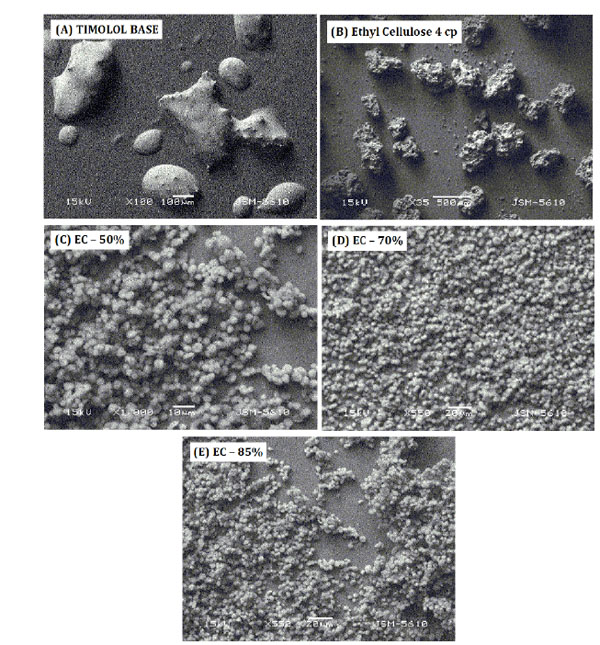
Extended Release of Timolol from Ethyl Cellulose Microparticles Laden Hydrogel Contact Lenses
Furqan A. Maulvi, Tejal G. Soni, Dinesh O. Shah
April 14, 2015
Design, Synthesis and Evaluation of Substituted 3-(1, 4-Diazepanyl)-Methyl-Phenyl-Sulphonamides as Potent 5-HT6 Antagonists in Cognitive Disorders
V.S. Velingkar, A.K. Chindhe, Mrunal Sanaye, Madhumangiri Gatane
June 30, 2016
Optimization of Bifonazole-Loaded Nisomal Formulation Using Plackett-Burman Design and 23 Factorial Design
Harshal Ashok Pawar, Vibhavari Bhaskar Attarde, Gide Parag Subhash
May 06, 2016
Structural Insights into the Molecular Design of HER2 Inhibitors
Avinash C. Tripathi, Pankaj Kumar Sonar, Ravindranath Rathore, Shailendra K. Saraf
July 29, 2016
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Stability Indicating Method for the Determination of Bromazepam Via its Copper (II) Chelates
Assefa Takele, Abdel-Maaboud I. Mohamed Attaya, Ariaya Hymete, Melisew Tadele Alula
April 28, 2017
Structural Features of Quercetin Derivatives by Using Pharmaco-phore Modeling Approach
Nixon Mendez, Md. Afroz Alam
June 06, 2016
Microwave Assisted Facile Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 2-Indolyl -1, 5-Benzothiazepines
Anna P. G. Nikalje, Mangesh S. Ghodke, Firoz A. K. Khan, Jaiprakash N. Sangshetti
June 22, 2016
Hydroxyl Ethyl Cellulose HHX and Polymethyl Methacrylate Based Site Specific Floating Delivery of Prochlorperazine Maleate
Swati C. Jagdale, Aleesha B. Randhave
July 28, 2016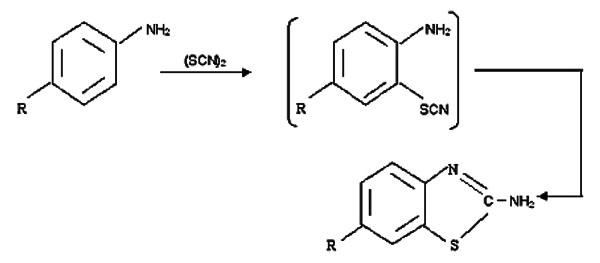
Antifungal Activities and Characterization of Some New Environmentally Safe Cu (II) Surfactants Substituted 2-Amino-6-Methyl Benzothiazole
Arun Kumar Sharma, Rashmi Sharma, Antima Gangwal
July 16, 2018
The Effect of Adding Indirect Relationship to Turbo Similarity Searching
Nurul H. A. Hassain Malim, Yong Pei-Chia, Marwah H. Al-Laila, Shereena M. Arif
June 15, 2016
Improvement in Dissolution of Bosentan Monohydrate by Solid Dispersions Using Spray Drying Technique
Pankaj V. Dangre, Vikesh B. Sormare, Mangesh D. Godbole
April 28, 2017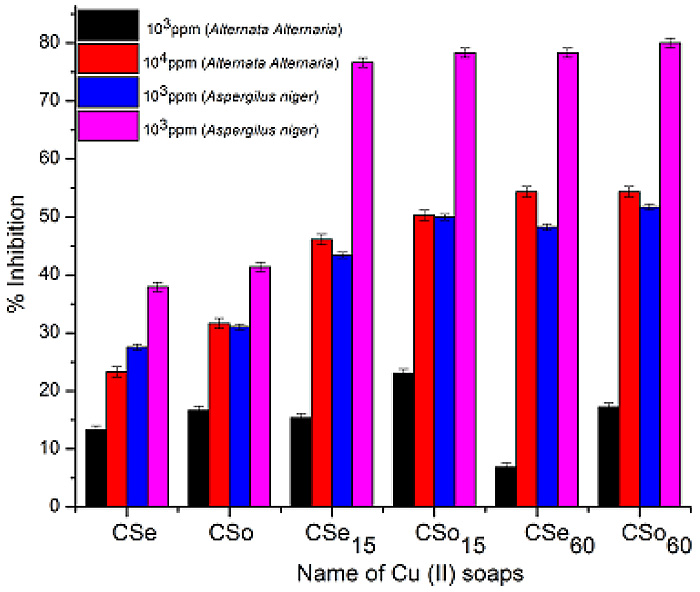
Antimicrobial Studies and Characterization of Copper Surfactants Derived from Various Oils Treated at High Temperatures by P.D.A. Technique
Renu Bhutra, Rashmi Sharma, Arun Kumar Sharma
November 14, 2018
Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Novel Mannich Bases Containing Pyrazole-5-One Phosphonates
V. E. Rani, L. K. Ravindranath
May 18, 2016