RESEARCH ARTICLE
Structural Features of Quercetin Derivatives by Using Pharmaco-phore Modeling Approach
Nixon Mendez, Md. Afroz Alam*
Article Information
Identifiers and Pagination:
Year: 2016Volume: 3
First Page: 79
Last Page: 98
Publisher Id: PHARMSCI-3-79
DOI: 10.2174/1874844901603010079
Article History:
Received Date: 22/5/2015Revision Received Date: 12/4/2016
Acceptance Date: 15/4/2016
Electronic publication date: 06/06/2016
Collection year: 2016
open-access license: This is an open access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 4.0 International Public License (CC BY-NC 4.0) (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode), which permits unrestricted, non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the work is properly cited.
Abstract
Background:
Quercetin which is a natural occurring flavonoid, exert a direct pro-apoptotic effect on tumor cells by blocking the growth of several cancer cell lines at different phases of the cell cycle. Quercetin derivatives have attracted considerable attention for their cytotoxity against human cancer cell lines. In this study the derivatives of Quercetin were used for docking followed by pharmacophore modeling for studying the 3D features and configurations responsible for biological activity of structurally diverse compounds.
Objective:
To develop a model which depicts the crucial structural features responsible for anti-lung cancer activities.
Method:
A robust pharmacophore developed for the receptor have been analyzed to identify potential areas of selectivity in the hyperspace of 3D pharmacophores that may lead to the discovery of anti-lung cancer drug or such compounds which could serve as templates for the design of new molecules as potential anti lung cancer agents.
Results:
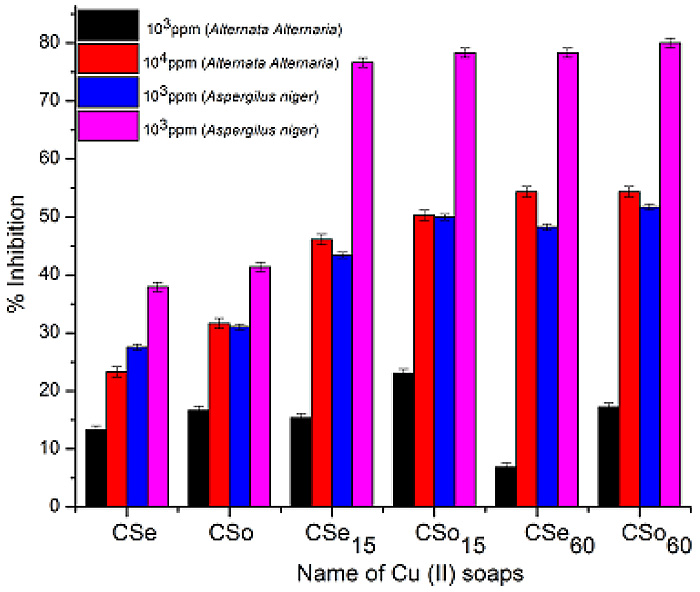
The generated best pharmacophore hypothesis yielded a statistically significant 3D-QSAR model, with a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.86 for training set and R2 = 0.76 for the test set molecules. The Cross validation regression coefficient is Q2 = 0.84 for training set and Q2 = 0.5 for test set molecules.
Conclusion:
The R2 and Q2 reveals that pharmacophore model provide insights into the structural and chemical features of the EGFR inhibitors of Quercetin derivatives that can be used as lead compound for further synthesis as well as for screening other similar novel inhibitors of EGFR.